
This type of reaction can be recognized because it involves a change in oxidation number of at least one element. Oxidation numbers are mainly used by chemists to identify and handle a type of chemical reaction called a redox reaction, or an oxidation-reduction reaction. If it only brought three of its own and is now sharing eight, it got more electrons than it gave, and it will have a negative charge.\,\] It brought four to share and got four from its neighbours in an even trade. If the atom brought four electrons of its own and it is now sharing eight, things are even.
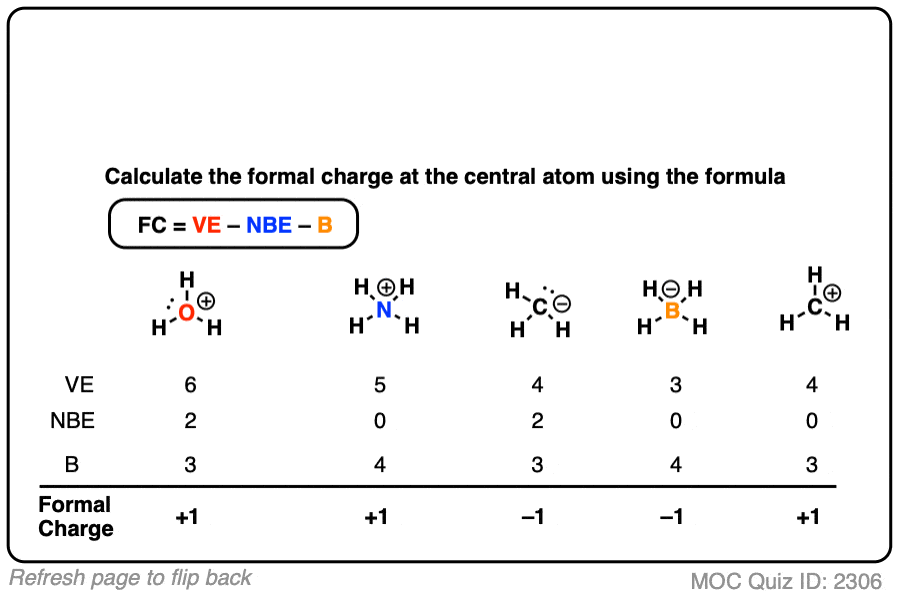
What we are really doing when we assign formal charge is comparing how many electrons the atom brought with it from the periodic table to how many it has now. These charges cancel to give an overall neutral molecule.
#Calculating formal charge co plus#
Oxygen has a plus charge and carbon has a minus charge. Notice that overall the carbon monoxide molecule is neutral. How did it get an octet with only three bonds? It got an extra electron from somewhere (the oxygen). Since it gives one of its electrons to carbon, it has formal charge +1.Ĭarbon has normal valence four, but here it is only making three bonds, even though it has an octet. If it is sharing a pair of electrons, we can think of it keeping one for itself and giving the other to carbon. It is sharing an extra pair of its electrons with carbon to make that third bond. Oxygen has normal valence two, but here it is making three bonds. With ten electrons total, the only way to get an octet on both atoms is to make three bonds between carbon and oxygen. There are no formal charges on the hydrogens either.Ĭarbon monoxide has a structure that is very similar to formaldehyde. Carbon has a normal valence of four, and it has four bonds here.

Oxygen has a normal valence of two, and it has two bonds in formaldehyde, so there is no formal charge on the oxygen. Calcium carbonate is found in limestone and chalk, for instance. Carbonate is an anion that is found in many forms. Carbon monoxide results from burning fossil fuels it is also an important industrial chemical used in manufacturing detergents. Formaldehyde (CH 2O) is a chemical that is used to preserve tissues you may be familiar with its odour from anatomy lab. To help us think about formal charges, let's look at a few small molecules that all contain carbon-oxygen multiple bonds but that are slightly different from each other.
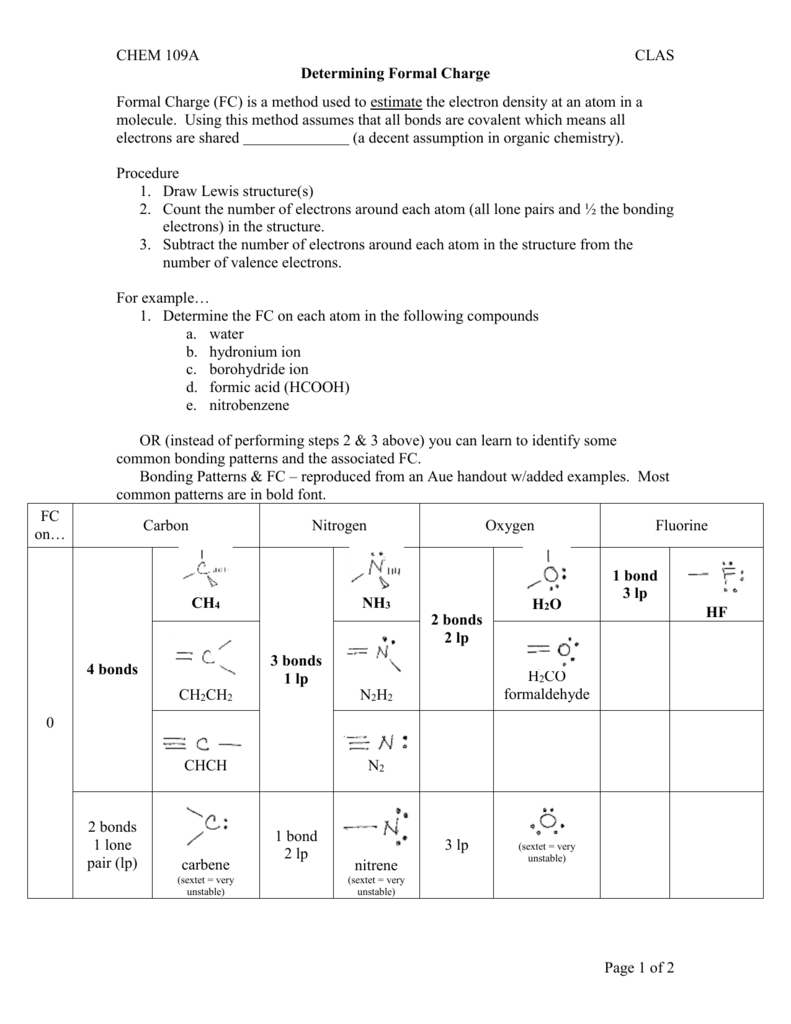
Old chemical bonds are broken when one atom takes the bonding electrons away from another atom. New chemical bonds are formed by sharing electrons. That is because reactivity has to do with the reorganization of electrons between atoms. One of the tools that we will eventually use to understand reactivity is formal charge. Looking at the structure of a molecule can help us to understand or to predict the behaviour of that compound.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
